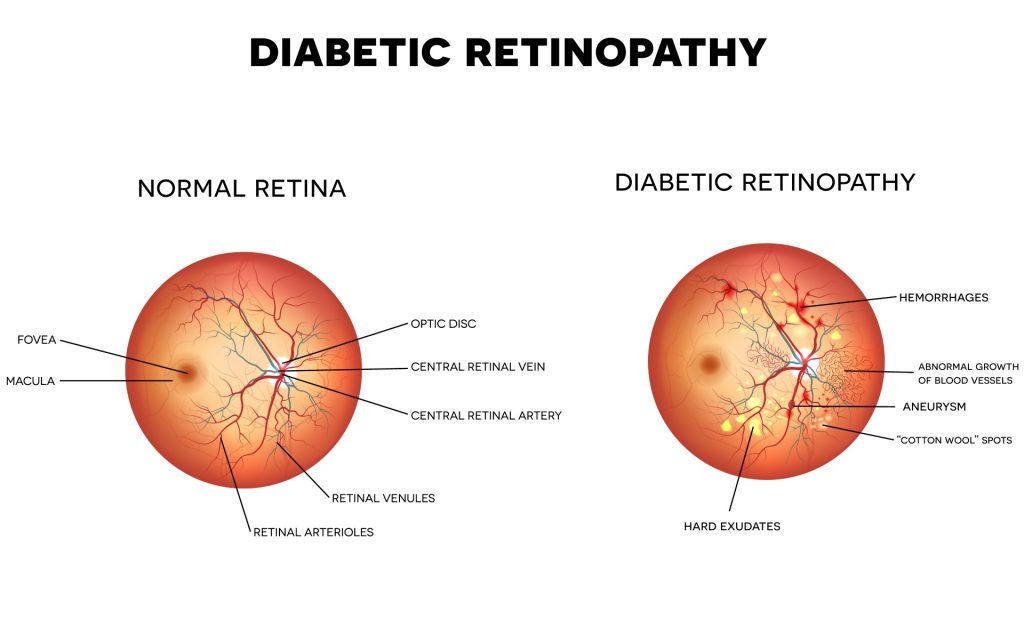
Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetic retinopathy is one of many complications from long standing elevated blood glucose levels. Long-term high blood glucose levels damage the fine blood vessels within the retina, which worsens with high blood pressure and high blood cholesterol levels.
Swelling of the macula in diabetics can present in any levels of diabetic retinopathy. Therefore, early detection of diabetic macular swelling is crucial to facilitate timely treatment.
Diabetic macular oedema (swelling) occurs due to the breakdown of the normal blood vessel architecture leading to fluid accumulation within the macula. It is crucial for the patient with diabetic macular oedema (DMO) to optimise blood glucose levels, blood pressure, blood cholesterol levels, weight and to avoid cigarette smoking. This is often managed jointly with the patient’s physician (GP and/or Diabetic Specialist).
Symptoms of serious diabetic retinopathy include blurred vision and floaters. The management option of DMO include eye injections (intravitreal therapy) with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF).



